Blog
Bridging Biology and Chemistry: BCL6, BMS-986458, and AI-Predicted Routes to Scalable Degraders
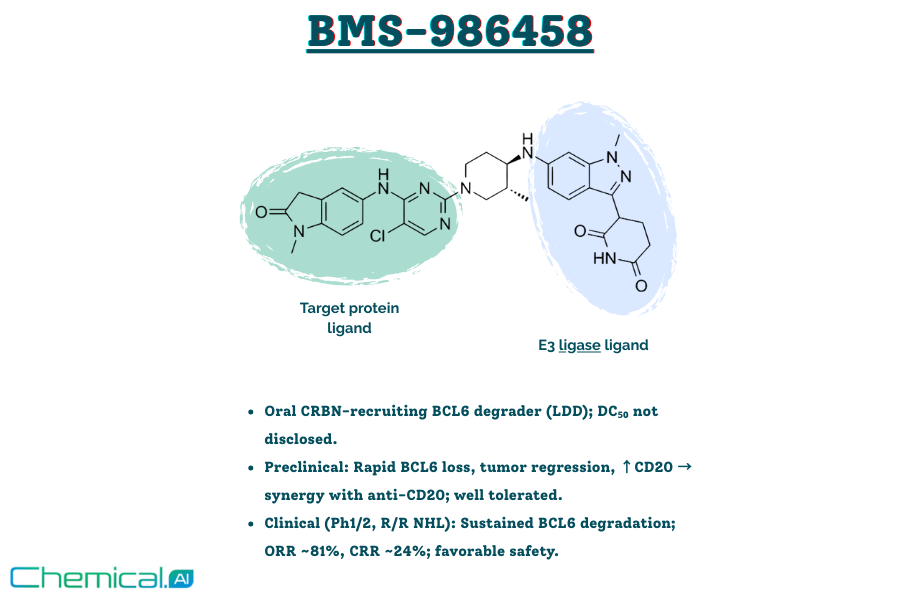
This blog explores the role of BCL6 as a central lymphoma driver and the clinical progress of Bristol Myers Squibb’s oral degrader BMS-986458. It also discusses AI-driven retrosynthesis tools like ChemAIRS, which propose palladium-free, scalable synthetic routes to overcome key challenges in PROTAC development.

ChemAIRS-Driven Retrosynthesis of Elironrasib (RMC-6291): A Next-Gen KRAS-G12C(ON) Inhibitor_EP20
The ChemAIRS platform successfully reconstructed a 25-step synthetic route to Revolution Medicines' groundbreaking KRAS inhibitor, elironrasib (RMC-6291). This next-generation therapeutic leverages a sanglifehrin-inspired macrocycle to form a stable tri-complex with KRAS-G12C(ON) and cyclophilin A (CypA), achieving exceptional selectivity through conformational rigidity.
Key ChemAIRS contributions:
Modular retrosynthesis: Deconstructed the macrocycle into two manageable fragments
Supply chain optimization: Identified commercially available starting materials
Risk mitigation: Flagged potential side reactions for synthetic planning
Route validation: Closely mirrored Revolution Medicines' published strategy
By combining macrocyclic drug design with AI-driven synthesis planning, ChemAIRS demonstrates how computational tools can accelerate the development of complex targeted therapies.
